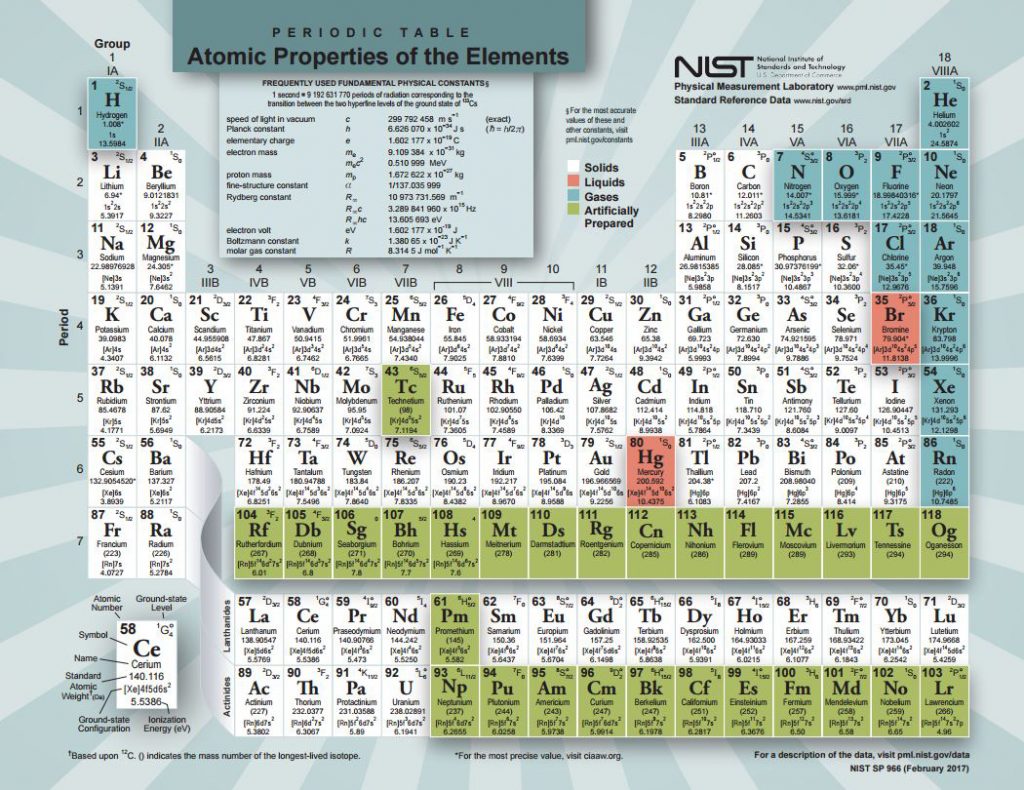
Periodic Table of Elements
A complete list of the elements with their descriptions as well as uses and occurrences (credit: elements.wlonk.com).
| Element | Description | Use or Occurrence | ||
| 1 | H | Hydrogen | explosive gas, lightest element | 90% of atoms in the universe, sun and stars, H2O life’s organic molecules |
| 2 | He | Helium | inert gas, second-lightest element | nuclear fusion in sun and stars, balloons, lasers, supercold refrigerant |
| 3 | Li | Lithium | lightest metal, soft, reactive | lightweight aluminum alloys, batteries, impact-resistant ceramic cookware, mood stabilizer |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium | lightweight metal | non-sparking copper alloy tools, aerospace, X-ray windows, beryl gems: emerald and aquamarines |
| 5 | B | Boron | hard black solid | borax soap fertilizer, stiff fibers, sports equipment (golf clubs, tennis rackets, skis), heat-resistant borosilicate glass (Pyrex©), semiconductors. |
| 6 | C | Carbon | hard diamond, soft graphite | basis of life’s organic molecules, animals, plants, C02, wood, paper, cloth, plastic, coal, oil |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen | colorless gas | 78% of air, organic molecules, protein, muscles, DNA, ammonia, fertilizer, explosives (TNT), refrigerants |
| 8 | O | Oxygen | colerless gas | 21% of air, H20, 65% of the human body, organic molecules, blood, breathing, fire, half of Earth’s crust, minerals, oxides |
| 9 | F | Flourine | yellowish poison gas, most reactive element | glowing fluorite, toothpaste, nonstick cookware (Teflon©), CFC refrigerants (Freon©) |
| 10 | Ne | Neon | intert gas | orange-red neon tubes for advertising signs, lasers, supercold refrigerant |
| 11 | Na | Sodium (Natrium) | soft metal, reactive | salt (NaCI), nerves, baking soda, antacids, lye, soap, soda ash, glass, papermaking, street lamps |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium | lightweight metal | chlorphyll in green plants, talc, basalt, aluminum alloys, cars, planes, bikes, flares, sparklers, antacids |
| 13 | Al | Aluminum | lightweight non-corroding metal | common metal, kitchenware, cans, foil, machinery, cars, planes, bikes, feldspar, granite, clay, ceramics, corundum, gems |
| 14 | Si | Silicon | hard metalloid | quartz, granite, sand, soil, clay, ceramics, glass, algae, diatoms, semiconductors, computer chips, silicone rubber |
| 15 | P | Phosphorus | glowing white waxy solid (also red and black forms) | bones, DNA, energy-storing phosphates (ATP), fertilizer, gypsum, rubber, acids, papermaking |
| 16 | S | Sulfur | brittle yellow solid | skin, hair, eggs, onions, garlic, skunks, hot springs, volcanos, gypsum, rubber, acids, papermaking |
| 17 | Cl | Chlorine | greenish poison gas | salt (NaCI), bleach, stomach acid, disinfectant, drinking water, swimming pools, PVC plastic pipes and bottles |
| 18 | Ar | Argon | inert gas | 1% of air, most abundant inert gas on Earth, light bulbs, “neon” tubes lasers, welding gas |
| 19 | K | Potassium (Kalium) | soft metal, reactive | salts, nerves, nutrient in fruits and vegetables, soap, fertilizer, potash, matches, gunpowder |
| 20 | Ca | Calcium | soft metal | bones, teeth, milk, leaves, vegetables, shells, coral, limestone, chalk, gypsum, plaster, mortar, cement, marble, antacids |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium | soft lightweight metal | aluminum alloys, racing bikes, stadium lamps, furnace bricks, aquamarines |
| 22 | Ti | Titanium | strongest lightweight metal, heat-resistant | aerospace, racing bikes, artificial joints, white paint, blue sapphires |
| 23 | V | Vanadium | hard metal | hard strong resilient steel, structures, vehicles, springs, driveshafts, tools, aerospace, violet sapphires |
| 24 | Cr | Chromium | hard shiny metal | stainless steel (Fe-Cr-Ni), kitchenware, nichrome heaters, car trim, paints, recording tape, emeralds, and rubies |
| 25 | Mn | Manganese | hard metal | hard tough steel, earthmovers, rock crushers, rails, plows, axes, batteries, fertilizer, amethysts |
| 26 | Fe | Iron (Ferrum) | medium-hard metal, magnetic | steel alloys are mostly iron, structures, vehicles, magnets, Earth’s core, red rocks, blood |
| 27 | Co | Cobalt | hard metal, magnetic | hard strong steel, cutting tools, turbines, magnets (Al-Ni-Co), blue glass and ceramics, vitamin B-12 |
| 28 | Ni | Nickel | medium hard metal, magnetic | stainless steel (Fe-Cr-Ni), kitchenware, nichrome heaters, coins, nicad batteries, Earth’s core |
| 29 | Cu | Copper (Cuprum) | colored metal, conducts heat and electricity well | wire, cookware, brass (Cu-Zn), bronze (Cu-Sn), coins, pipes, blue crab blood |
| 30 | Zn | Zinc | non-corroding metal | galvanized steel, brass (Cu-Zn), batteries, white paint, phosphors in TVs and lamps, fertilizer |
| 31 | Ga | Gallium | soft metal, melts on a hot day | semiconductors, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) (GaAs), signal lights, tiny lasers |
| 32 | Ge | Germanium | brittle metalloid | semiconductors, transistors, rectifiers, diodes, photocells, lenses, infrared windows |
| 33 | As | Arsenic | brittle metalloid | poisons, semiconductors, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) (GaAs), signal lights, tiny lasers |
| 34 | Se | Selenium | brittle gray solid | semiconductors, photocopiers, laser printers, photocells, red glass, dandruff shampoo, rubber |
| 35 | Br | Bromine | dark red liquid | disinfectant, pools and spas, photo film, flame retardant, leaded gas, sedatives |
| 36 | Kr | Krypton | inert gas | high-intensity lamps, headlights, flashlights, lanterns, “neon” tubes, lasers |
| 37 | Rb | Rubidium | soft metal, reactive | atomic clocks, global navigation (GPS), vacuum tube scavenger |
| 38 | St | Strontium | soft metal | red fireworks, flares, phosphors, nuclear batteries, medical diagnostic tracer, nuclear fallout |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium | soft metal | phosphors in color TVs, lasers (YAG, YLF), furnace bricks, high-temperature superconductors |
| 40 | Zr | Zirconium | non-corroding neutron-resistant metal | chemical pipelines, nuclear reactors, furnace bricks, abrasives, zircon gems |
| 41 | Nb | Niobium | high-melting-point, non-corroding metal | chemical pipelines, superconductors, magnetic levitation trains, MRI magnets |
| 42 | Mo | Molybdenum | high-melting-point metal | hard steel, cutting tools, drill bits, armor plate, gun barrels, fertilizers |
| 43 | Tc | Technetium | radioactive, long-lived | first artificially made element, only traces on Earth but found in stars, medical diagnostic tracer |
| 44 | Ru | Ruthenium | non-corroding hard metal | electric contacts, leaf switches, pen tips, catalyst, hydrogen production |
| 45 | Rh | Rhodium | non-corroding hard shiny metal | labware, reflectors, electric contacts, thermocouples, catalyst, pollution control |
| 46 | Pd | Palladium | non-corroding hard metal, absorbs hydrogen | labware, electric contacts, dentistry, catalyst, pollution control |
| 47 | Ag | Silver (Argentum) | soft shiny metal, conducts electricity best of all elements | jewelry, silverware, coins, dentistry, photo film |
| 48 | Cd | Cadmium | non-corroding soft metal, toxic | electroplated steel, nicad batteries, red and yellow paints, fire sprinklers |
| 49 | In | Indium | soft metal | solders, glass seals, glass coatings, liquid crystal displays (LCD), semiconductors, diodes, photocells |
| 50 | Sn | Tin (Stanum) | non-corroding soft metal | solders, plated food cans, bronze (Cu-Sn), pewter cups, glassmaking, fire sprinklers |
| 51 | Sb | Antimony (Stibium) | brittle metalloid | solders, lead hardener, batteries, bullets, semiconductors, photocells, matches, flame retardant |
| 52 | Te | Tellurium | brittle metalloid | alloys, semiconductors, photocopiers, computer disk, thermo-electric coolers and generators |
| 53 | I | Iodine | violet-black solid | disinfectant for wounds and drinking water, added to salt to prevent thyroid disease, photo film |
| 54 | Xe | Xenon | inert gas | high-intensity lamps, headlights, stadium lamps, projectors, strobes, lasers, spacecraft ion engines |
| 55 | Cs | Cesium | soft metal, melts on a hot day, reactive, largest stable atoms | atomic clocks, global navigation (GPS), vacuum tube scavenger |
| 56 | Ba | Barium | soft metal, absorbs X-rays | stomach X-ray contrast enhancer, green fireworks, whitener and filler for paper |
| 57 | La | Lanthanum | soft metal | optical glass, telescope eyepieces, camera lenses, lighter flints, arc lams |
| 58 | Ce | Cerium | soft metal | most abundant rare earth metal, lighter flints, arc lamps, gas lamp mantles, self-cleaning ovens, glass polishing |
| 59 | Pr | Praseodymium | soft metal | torchworkers’ didymium eyeglasses, lighter flints, arc lamps, magnets, yellow glass |
| 60 | Nd | Neodymium | soft metal | strong magnets (Nd-Fe-B), electric motors, speakers and headphones, lasers, lighter flints |
| 61 | Pm | Promethium | radioactive, long-lived | human-made, small traces in nature, luminous dials, sheet thickness gauges |
| 62 | Sm | Samarium | soft metal | magnets (Sm-Co), electric motors, speakers and headphones, infrared sensors, infrared absorbing glass |
| 63 | Eu | Europium | soft metal | phosphors in color TVs and trichromatic fluorescent lamps, luminous paint, lasers |
| 64 | Gd | Gadolinium | soft metal, best neutron absorber, magnetic | magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast enhancer, phosphors, neutron radiography |
| 65 | Tb | Terbium | soft metal | phosphors in color TVs and trichromatic fluorescent lamps, computer disks, magnetostrictive “smart” materials (Fe-Dy-Tb) (Terfenol-D©) |
| 66 | Dy | Dysprosium | soft metal | nuclear control rods, MRI phosphors, computer disks, magnetostrictive “smart” materials (Fe-Dy-Tb) (Terfenol-D©) |
| 67 | Ho | Holmium | soft metal | infrared lasers, laser surgery, eye-safe laser rangefinders, computer disks, yellow glass filters |
| 68 | Er | Erbium | soft metal | fiber optic signal amplifiers, infrared lasers, laser surgery, pink glass, sunglasses, vanadium alloys |
| 69 | Tm | Thulium | soft metal | rarest stable rare earth metal, infrared lasers, laser surgery, phosphors |
| 70 | Yb | Ytterbium | soft metal | fiber optic signal amplifiers, infrared fiber lasers, stainless steel alloys |
| 71 | Lu | Lutetium | soft metal | densest and hardest rare earth metal , cancer fighting photodynamic (light-activated) medicine |
| 72 | Hf | Hafnium | non-corroding metal, absorbs neutrons | nuclear reactor control rods in submarines, plasma torch electrodes |
| 73 | Ta | Tantalum | high-melting-point non-corroding metal | labware, surgical tools, artificial joints, capacitors, mobile phones |
| 74 | W | Tungsten (Wolfram) | highest-melting-point metal, dense | filaments in lamps and TVs, cutting tools, abrasives, thermocouples |
| 75 | Re | Renium | high-melting-point dense metal | rocket engines, heater coils, laboratory filaments, electric contacts, thermocouples, catalyst |
| 76 | Os | Osmium | non-corroding high-melting-point hard metal, densest element (same as Ir) | electric contacts, pen tips, needles, fingerprint powder |
| 77 | Ir | Iridium | non-corroding hard metal, densest element (same as Os) | labware, spark plugs, pen tips, needles |
| 78 | Pt | Platinum | non-corroding dense metal | labware, spark plugs, catalyst, pollution control, petroleum cracking, processing fats |
| 79 | Au | Gold (Aurum) | most malleable element, dense non-tarnishing colored metal | jewelry, coins, ultra-thin gold leaf, electric contacts |
| 80 | Hg | Mercury | liquid metal, toxic | thermometers, barometers, thermostats, street lamps, fluorescent lamps, dentistry |
| 81 | Tl | Thallium | soft metal, toxic | low-melting-point mercury alloys, low-temperature thermometers, udersea lamps, photocells |
| 82 | Pb | Lead (Plumbum) | dense, soft, non-corroding metal, toxic | weights, solders, batteries, bullets, crystal glass, old plumbing, radiation shield |
| 83 | Bi | Bismuth | low melting point, brittle metal | solders, fuses, fire sprinklers (plugs melt when hot), cosmetics pigment |
| 84 | Po | Polonium | radioactive, long-lived | first radioactive element found, small traces in nature, anti-static brushes, tobacco |
| 85 | At | Astatine | radioactive, short-lived | small traces in nature, cancer medicine |
| 86 | Rn | Radon | radioactive gas, short-lived | environmental hazard, surgical implants for cancer treatment |
| 87 | Fr | Francium | radioactive, short-lived, atoms larger than cesium | small traces in nature, studied in laser atom traps |
| 88 | Ra | Radium | radioactive, long-lived | luminous watches (now banned), medical radon production, radiography, radwaste |
| 89 | Ac | Actinium | radioactive, long-lived | small traces in nature, cancer medicine, neutron source, radwaste |
| 90 | Th | Thorium | radioactive, long-lived | most abundant radioactive element, nuclear reactor fuel, gas lamp mantles, tungsten filaments, radwaste |
| 91 | Pa | Protactinium | radioactive, long-lived | small traces in nature, no uses, radwaste |
| 92 | U | Uranium | radioactive, long-lived, dense | nuclear reactor fuel, nuclear weapons, counterweights, armor piercing bullets |
| 93 | Np | Neptunium | radioactive, long-lived | small traces in nature, neutron detectors, dosimeters, possibly nuclear weapons, radwaste |
| 94 | Pu | Plutonium | radioactive, long-lived | small traces in nature, nuclear reactor fuel, spacecraft power, nuclear weapons |
| 95 | Am | Americium | radioactive, long-lived | never found in nature, smoke detectors, sheet thickness gauges, radwaste |
| 96 | Cm | Curium | radioactive, long-lived | never found in nature, scientific instruments, mineral analyzers, radwaste |
| 97 | Bk | Berkelium | radioactive, long-lived | never found in nature, no uses, radwaste |
| 98 | Cf | Californium | radioactive, long-lived | never found in nature, scientific instruments, mineral analyzers, radwaste |
| 99 | Es | Einsteinium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 100 | Fm | Fermium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 101 | Md | Mendelevium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 102 | No | Nobelium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 103 | Lr | Lawrencium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 104 | Rf | Rutherfordium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 105 | Db | Dubnium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 106 | Sg | Seaborgium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 107 | Bh | Bohrium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 108 | Hs | Hassium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 109 | Mt | Meitnerium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 110 | Ds | Darmstadtium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 111 | Rg | Roentgenium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 112 | Cn | Copernicium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 113 | Nh | Nihonium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 114 | Fl | Flerovium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 115 | Mc | Moscovium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 116 | Lv | Livermorium | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 117 | Ts | Tennessine | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
| 118 | Og | Oganessan | radioactive, short-lived | never found in nature, no uses |
Sources & More Resources
2017 Periodic Table of Elements Source: NIST
Interactive Periodic Table of Elements along with Elements Descriptions, Uses & Occurrences Source with much more in-depth information: elements.wlonk.com
History and uses of each individual element: Jefferson Lab – It’s Elemental
More information about the Periodic Table of Elements: Encyclopedia Britannica
Printable periodic table of elements (Multiple versions): Science Notes
Also, see our Industry Term Glossary and ESDA Glossary of Terms